AI Agent 协议
- 1: MCP
- 1.1: MCP 介绍
- 1.1.1: MCP 定义
- 1.2: Datalog
- 1.2.1: 介绍
- 1.2.2: mcpcatalog.io
- 1.2.3: Docker MCP Catalog
- 1.2.3.1: 介绍
- 1.2.3.2: Docker MCP Datalog与工具包发布
- 1.2.3.3: 轻松构建更智能的 AI 代理
- 2: A2A
- 2.1: A2A 介绍
- 2.2: A2A Card
- 2.2.1: A2A Card 介绍
- 3: Agent Skills
- 3.1: Agent Skills文章
- 3.1.1: 为智能体配备 Agent Skills 以适应真实世界
1 - MCP
1.1 - MCP 介绍
1.1.1 - MCP 定义
1.2 - Datalog
1.2.1 - 介绍
1.2.2 - mcpcatalog.io
介绍
MCP
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard for connecting AI assistants to the systems where data lives, enabling context-aware AI applications.
模型上下文协议(Model Context Protocol / MCP)是一个开放标准,用于将人工智能助手与数据所在的系统连接,从而实现具有上下文意识的人工智能应用。
MCP datalog
Connect AI assistants to your data sources with the open standard for context-aware AI. Explore MCP servers and implementations.
通过开放标准将人工智能助手与您的数据源连接,实现基于上下文的人工智能。探索MCP服务器及实现方案。
?
推荐的MCP服务器
探索预先构建的MCP服务器,适用于连接AI助手与您的数据源的流行企业系统。
-
API Connect
A comprehensive API management solution that allows businesses to create, secure, manage, and socialize APIs across their organization.
一个全面的API管理解决方案,使企业能够在整个组织内创建、保护、管理和共享API。
-
DataFlow
A fully managed data processing service that enables simple, flexible, and reliable ETL pipelines.
一个完全托管的数据处理服务,可实现简单、灵活且可靠的ETL管道。
-
EventStream
A scalable event streaming platform for building real-time data pipelines and streaming applications.
一个可扩展的事件流平台,用于构建实时数据管道和流式应用程序。
-
Prediction API
A service that makes it easy to deploy machine learning models and get predictions via API calls.
一项服务,可轻松部署机器学习模型并通过API调用获取预测结果。
Browse by Category
Explore MCP servers and implementations organized by category to find the perfect solution for your AI integration needs.
按类别浏览
按类别浏览MCP服务器和实现方案,以找到满足您人工智能集成需求的完美解决方案。
1.2.3 - Docker MCP Catalog
https://docs.docker.com/ai/mcp-catalog-and-toolkit/catalog/
Docker MCP 目录是一个集中化、可信赖的注册中心,用于发现、共享和运行兼容 MCP 的工具。它与 Docker Hub 无缝集成,提供经过验证、版本化且精心筛选的 MCP 服务器,这些服务器均打包为 Docker 镜像。该目录也可在 Docker Desktop 中使用。
该目录解决了 MCP 服务器的常见难题:
-
环境冲突:工具通常需要特定运行时环境,可能与现有配置产生冲突。
-
缺乏隔离性:传统配置方式存在暴露主机系统的风险。
-
配置复杂性:手动安装和配置导致采用速度缓慢。
-
跨平台不一致性:工具在不同操作系统上可能出现不可预测的行为。
借助 Docker,每个 MCP 服务器都作为独立容器运行,因此具有可移植性、隔离性和一致性。您可以通过 Docker CLI 或 Docker Desktop 即时启动工具,无需担心依赖项或兼容性问题。
核心特性
-
一站式提供 100 多个经过验证的 MCP 服务器
-
发布者验证与版本化发布
-
基于 Docker 基础设施的拉取式分发
-
由 New Relic、Stripe、Grafana 等合作伙伴提供的工具
工作原理
MCP 目录中的每个工具都打包为带有元数据的 Docker 镜像
- 通过 Docker Hub 的 mcp/ 命名空间发现工具。
- 通过 MCP Toolkit 进行简单配置,将工具连接到其首选代理。
- 使用 Docker Desktop 或 CLI 拉取并运行工具。
每个目录条目提供:
- 工具描述与元数据
- 版本历史
- agent 集成示例配置
从目录中使用 MCP 服务器
要从目录中使用 MCP 服务器,请参阅 MCP 工具包。
向目录贡献 MCP 服务器
若要将 MCP 服务器添加到 Docker MCP 目录,请填写 Docker MCP 提交表单。
1.2.3.1 - 介绍
https://docs.docker.com/ai/mcp-catalog-and-toolkit/catalog/
Docker MCP 目录是一个集中化、可信赖的注册中心,用于发现、共享和运行兼容 MCP 的工具。它与 Docker Hub 无缝集成,提供经过验证、版本化且精心筛选的 MCP 服务器,这些服务器均打包为 Docker 镜像。该目录也可在 Docker Desktop 中使用。
该目录解决了 MCP 服务器的常见难题:
-
环境冲突:工具通常需要特定运行时环境,可能与现有配置产生冲突。
-
缺乏隔离性:传统配置方式存在暴露主机系统的风险。
-
配置复杂性:手动安装和配置导致采用速度缓慢。
-
跨平台不一致性:工具在不同操作系统上可能出现不可预测的行为。
借助 Docker,每个 MCP 服务器都作为独立容器运行,因此具有可移植性、隔离性和一致性。您可以通过 Docker CLI 或 Docker Desktop 即时启动工具,无需担心依赖项或兼容性问题。
核心特性
-
一站式提供 100 多个经过验证的 MCP 服务器
-
发布者验证与版本化发布
-
基于 Docker 基础设施的拉取式分发
-
由 New Relic、Stripe、Grafana 等合作伙伴提供的工具
工作原理
MCP 目录中的每个工具都打包为带有元数据的 Docker 镜像
- 通过 Docker Hub 的 mcp/ 命名空间发现工具。
- 通过 MCP Toolkit 进行简单配置,将工具连接到其首选代理。
- 使用 Docker Desktop 或 CLI 拉取并运行工具。
每个目录条目提供:
- 工具描述与元数据
- 版本历史
- agent 集成示例配置
从目录中使用 MCP 服务器
要从目录中使用 MCP 服务器,请参阅 MCP 工具包。
向目录贡献 MCP 服务器
若要将 MCP 服务器添加到 Docker MCP 目录,请填写 Docker MCP 提交表单。
1.2.3.2 - Docker MCP Datalog与工具包发布
https://www.docker.com/blog/announcing-docker-mcp-catalog-and-toolkit-beta/
模型上下文协议(MCP)正迅速成为连接 AI 智能体与外部工具的标准,但开发者体验尚未同步跟进。当前存在发现渠道碎片化、配置流程笨拙、安全措施往往事后补丁等问题。改善这一体验非单打独斗可成——需要全行业共同努力。构建安全、可扩展且可信的 MCP 生态系统,必须实现跨平台与供应商的协作。
为此,我们兴奋地宣布 Docker MCP datalog与工具包现已开放 Beta 测试。作为 Docker Hub 的新成员,Docker MCP 目录是您探索的起点,它精选呈现了一系列热门的容器化 MCP 服务器,助您快速启动智能体 AI 开发。但仅有发现功能还不够——这正是 MCP 工具包的用武之地。该工具包能简化安装流程、管理凭证、实施访问控制并保障运行时环境安全。Docker MCP datalog与工具包双剑合璧,为开发者和团队提供了完整的 MCP 工具使用基础,让这些工具更易发现、更安全使用,并能轻松跨项目和团队扩展。
我们正与 Stripe、Elastic、Heroku、Pulumi、Grafana Labs、Kong Inc.、Neo4j、New Relic、Continue.dev 等云计算、开发者工具及 AI 领域最受信赖的伙伴携手,共同构建安全的 MCP 工具生态系统。通过 Docker Desktop 一键连接 Gordon(Docker AI 智能体)、Claude、Cursor、VSCode、Windsurf、continue.dev 和 Goose 等主流 MCP 客户端,打造强大智能的 AI 智能体从未如此简单。
这完全契合我们的使命。Docker 开创了容器革命,彻底改变了开发者构建和部署软件的方式。如今,超过 2000 万注册开发者依赖 Docker 来构建、共享和运行现代应用程序。现在,我们将把同样值得信赖的体验带到下一个前沿领域:搭载 MCP 工具的智能体 AI。
模型上下文协议(MCP)发展势头正劲——还有哪些方面需要改进?
随着 MCP 成为智能体 AI 系统的支柱,开发者体验仍面临关键挑战。以下是当前存在的主要障碍:
-
难以发现合适、官方且/或可信的工具
寻找 MCP 服务器的渠道十分分散。开发者需要在各类注册中心、社区维护列表和博客文章间反复搜索——却依然难以辨别哪些是官方可信的服务器。
-
复杂的安装与分发流程
MCP 工具的入门门槛依然很高。开发者通常需要克隆代码仓库,在 Node.js 或 Python 等环境中解决依赖冲突,还要自行托管本地服务——其中许多服务并未容器化,这使得配置和移植更加困难。更麻烦的是,连接 MCP 客户端会带来更多阻碍,每个客户端都需要定制化配置,严重拖慢了上手速度。
-
认证与权限机制存在缺陷
许多 MCP 工具在运行时拥有对主机的完全访问权限,通过 npx 或 uvx 启动,缺乏隔离或沙箱保护。凭证通常以明文环境变量形式传递,导致敏感数据暴露并增加泄露风险。此外,这些工具往往未针对规模化和安全性进行设计,缺少企业级功能如策略执行、审计日志和标准化安全措施。
Docker 如何助力解决这些挑战
Docker MCP 目录与工具包旨在通过安全简化 MCP 服务器的发现、安装和认证流程,解决上述痛点——让您轻松连接喜爱的 MCP 客户端。
在安全隔离的容器中轻松发现并运行 MCP 服务器
MCP 目录让您能便捷发现并访问 100 多种 MCP 服务器——包括 Stripe、Elastic、Neo4j 等众多服务,所有资源均可在 Docker Hub 获取。通过 MCP Toolkit 的 Docker Desktop 扩展插件,您能快速安全地运行这些服务器并与之交互。将 MCP 服务器容器化后,开发者可规避运行时配置、依赖冲突和环境不一致等常见难题——只需运行容器,即可开箱即用。
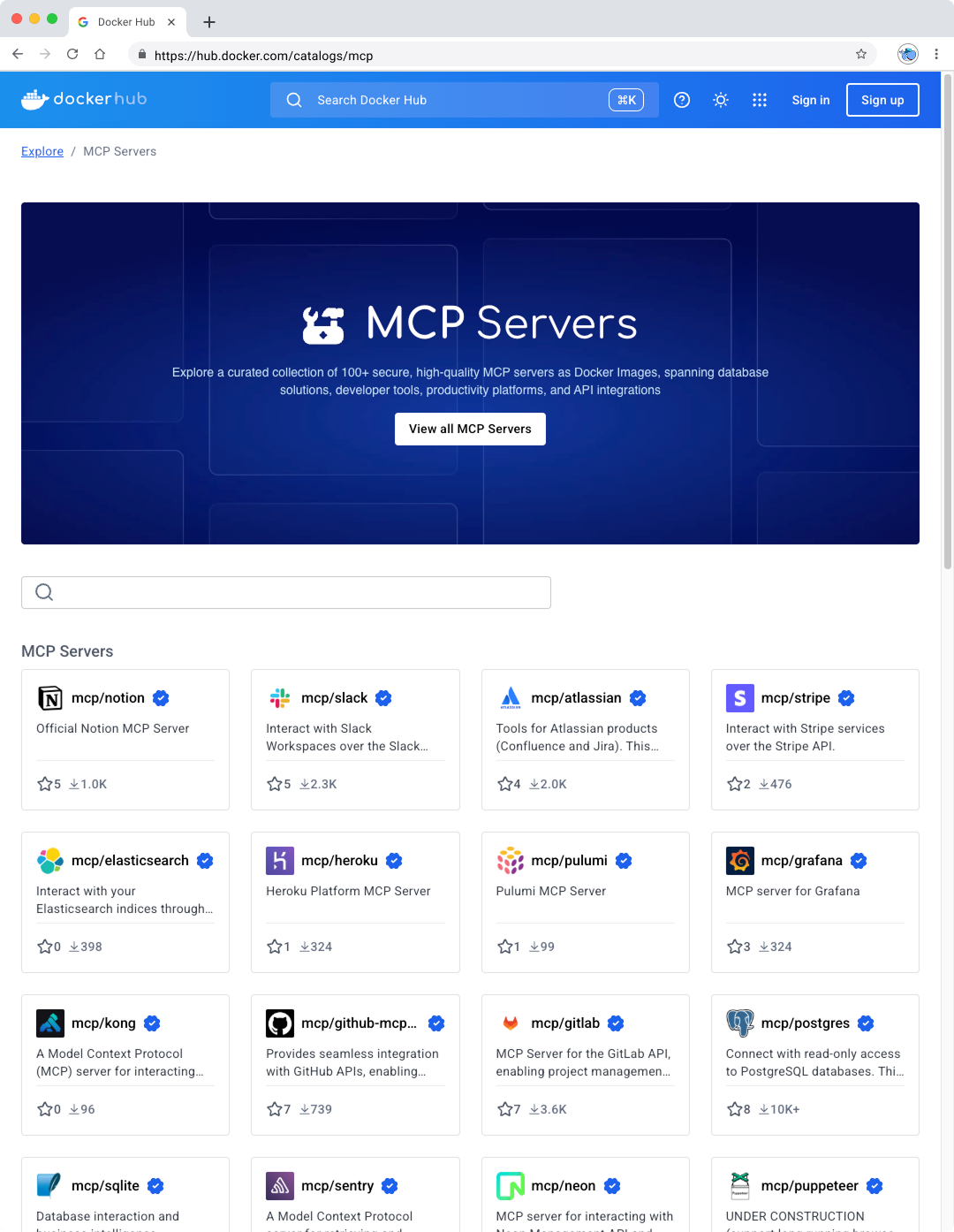
图 1:在 Docker Hub 的 Docker MCP 目录中发现精选和热门的 MCP 服务器
我们不仅简化了发现和安装流程——更将安全性置于 MCP 体验的核心。由于 MCP 运行在 Docker 容器镜像内,它们继承了开发者早已信赖的内置安全特性,以及贯穿软件供应链的丰富安全工具生态。我们更进一步:Docker MCP 工具包通过发挥 Docker 作为安全内容与安全运行时提供者的双重优势,专门应对 MCP 服务器特有的新兴威胁,如工具投毒和工具撤池攻击。
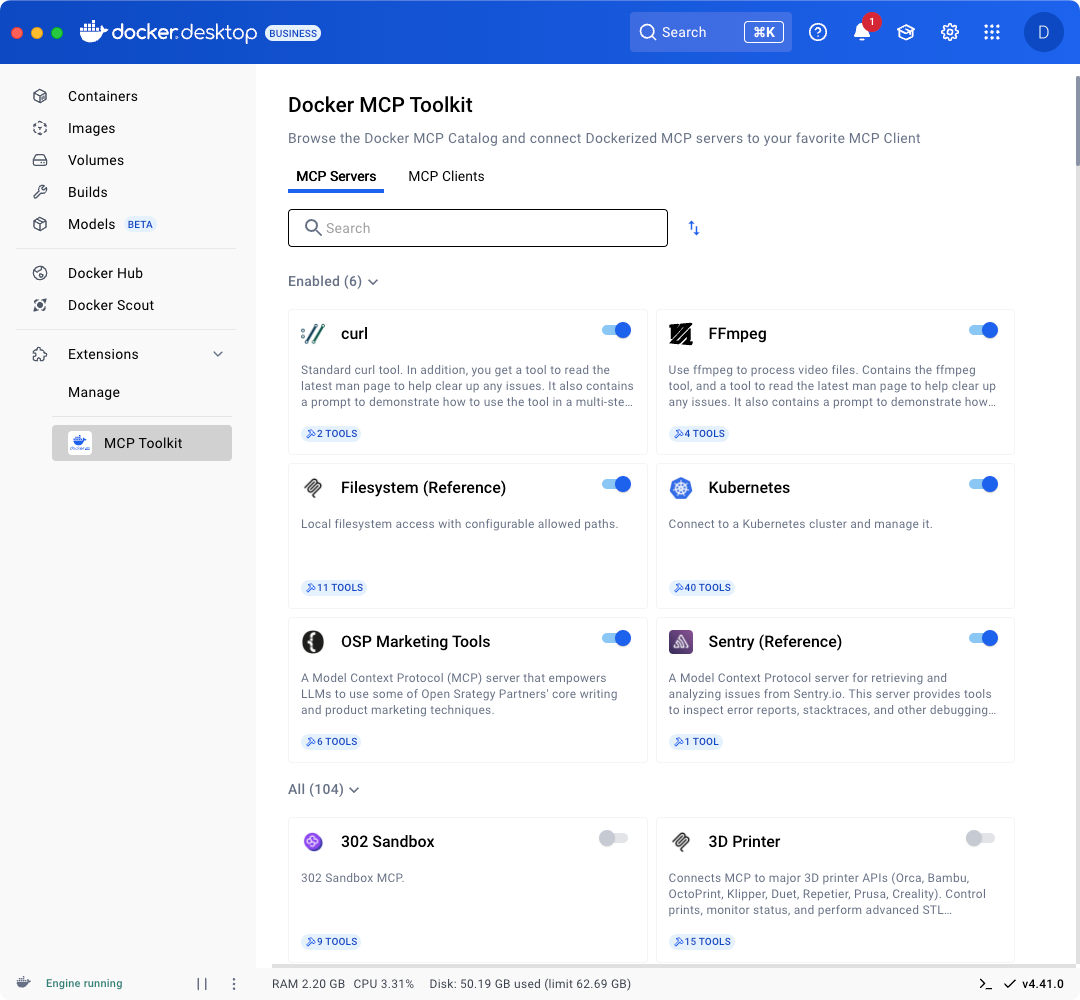
图 2:MCP 工具包 Docker 桌面扩展让您能够轻松安全地在容器中运行 MCP 服务器。
前往 Docker Desktop 的扩展菜单即可开始使用 Docker MCP 目录和工具包,或通过此链接进行安装。查看我们的文档以获取更多信息。
一键式 MCP 客户端集成与内置安全认证
精选的 MCP 列表和简化的安全设置固然是良好的开端,但这仅仅是个开始。您可以将 Docker MCP 目录中的热门 MCP 服务器连接至任何 MCP 客户端。对于 Gordon(Docker AI 助手)、Claude、Cursor、VSCode、Windsurf、continue.dev 和 Goose 等客户端,一键设置功能将实现无缝集成。
Docker MCP 工具包内置 OAuth 支持与安全凭证存储功能,使客户端无需将密钥硬编码到环境变量中即可完成 MCP 服务器及第三方服务的认证。这确保您的 MCP 工具从一开始就能安全可靠地运行。
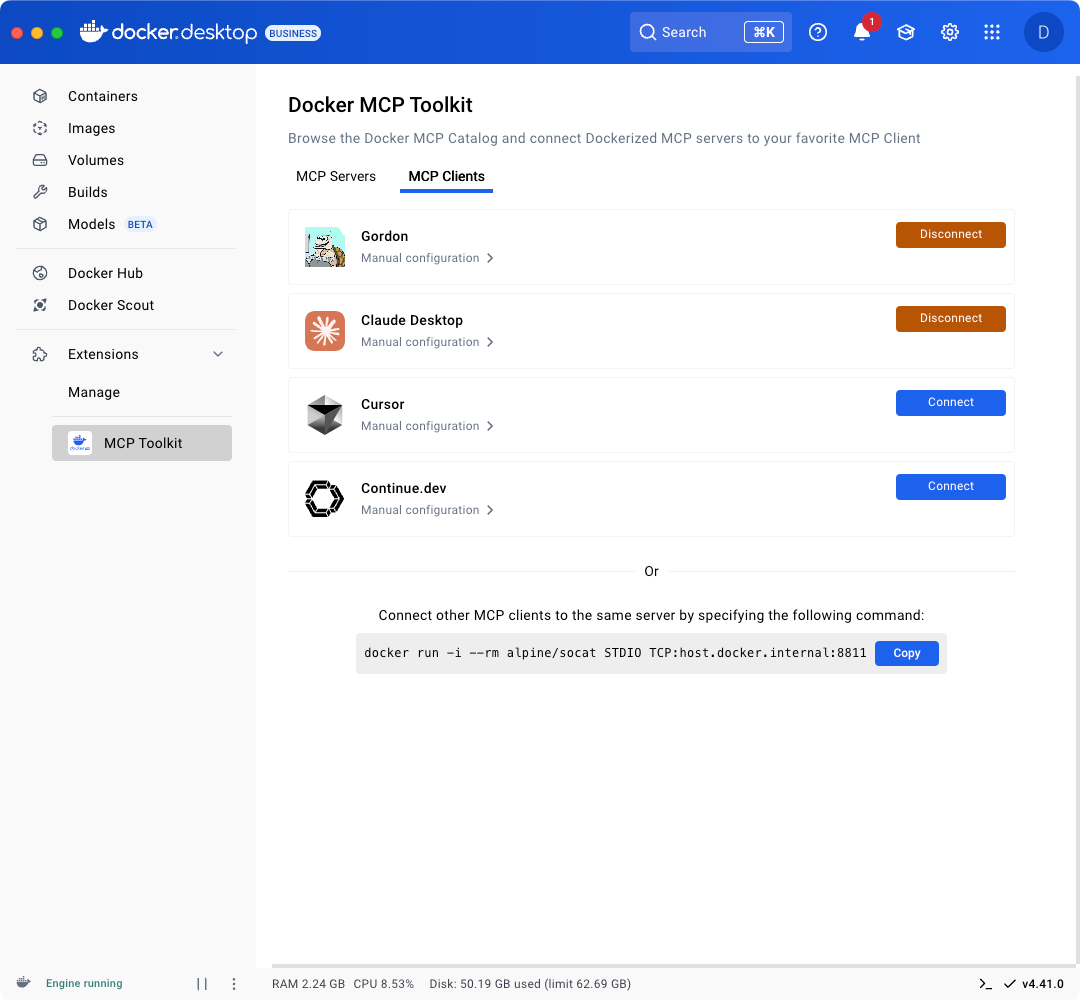
图 3:只需点击一下,即可轻松连接至您喜爱的 MCP 客户端,如 Gordon、Claude、Cursor 和 continue.dev。
企业级 MCP 工具链:在 Docker Hub 上构建、管理和共享
很快,您将能在 Docker Hub 上构建和共享自己的 MCP——这个托管着超 1400 万镜像、拥有数百万活跃用户及强大可信内容生态的平台。团队依赖 Docker Hub 获取经过验证的镜像、深度镜像分析、生命周期管理和企业级工具。这些同样值得信赖的功能即将扩展至 MCP 领域,让团队能获取最新工具,并以安全可靠的方式分发自己的 MCP。与容器镜像类似,MCP 也将集成注册表访问管理、镜像访问管理等企业功能,确保端到端的安全高效开发者工作流。
总结
Docker MCP datalog 与工具包为快速发展的 MCP 工具领域带来了亟需的体系化架构、安全保障和操作简捷性。通过标准化 MCP 服务器的发现、安装与安全配置流程,我们为开发者消除了构建更智能、更强大 AI 驱动应用与代理时的技术障碍。
无论您需要连接外部工具、定制工作流,还是在 IDE 内扩展自动化能力,Docker 都能让整个过程既简单又安全。而这仅仅是个开始。通过持续投入扩展 MCP 生态系统并优化工具管理方式,我们致力于让每个团队都能便捷使用强大的 AI 工具链。
借助 Docker 目录与工具包,您的 AI 代理将不再受限于内置功能——任何可接入的组件都能成为其能力延伸。
立即前往 Docker Desktop 的扩展菜单启用 Docker MCP 目录与工具包,或通过此链接直接安装。您还可在我们即将举办的网络研讨会中观看实际演示。有意在 Docker 上托管您的 MCP 服务器?欢迎随时联系我们。
补充
-
专为简便与安全而设计
agentic AI 的核心是 MCP 工具,但使用它们不应带来麻烦。Docker的 MCP datalog 和工具包让使用过程既简单又安全。
-
加速代理型人工智能开发,借助 Docker MCP datalog与工具包
无论您是在开发人工智能驱动的应用程序还是代理,MCP 目录都能为您提供经过精心筛选的可信服务器,助您快速入门。您可以将 MCP 服务器与 Docker AI Agent、Claude、Cursor、VS Code、Windsurf、continue.dev 和 Goose 等客户端快速且安全地连接。MCP工具包在后台处理设置、身份验证和安全事宜,让您能够专注于核心任务。基于Docker Hub构建,它是一个可靠的平台,用于上传、存储和管理MCP服务器,提供企业级安全性和控制力。
1.2.3.3 - 轻松构建更智能的 AI 代理
https://dev.to/docker/docker-mcp-catalog-toolkit-building-smarter-ai-agents-with-ease-408c
引言:Docker MCP 是什么及其重要性
由 ChatGPT、Claude 和定制 LLMs 驱动的基于智能体的 AI 应用兴起,催生了对与现实世界工具进行模块化、安全且标准化集成的需求。Docker 的模型上下文协议(MCP)及其目录与工具包正是为此而生。
Docker 正将自身定位不仅作为容器平台,更是智能代理的基础设施支柱。本文将探讨 MCP 架构、目录和工具包,并演示如何构建自己的 MCP 服务器。
理解 MCP——模型上下文协议
What it is: 它是什么:
- MCP 是一种开放协议,允许 AI 客户端(如智能体)安全且可预测地调用现实世界服务。
- 该协议专为实现工具互操作性、安全凭证管理(处理 API 密钥和令牌)以及基于容器的执行而设计。
Why it matters: 为何重要:
- 缺乏 MCP 这类标准,智能体只能依赖脆弱的 API 或不安全的插件。
- Docker 通过容器化技术为这些服务提供了安全隔离的运行环境。
Visual overview: 可视化概览:
AI 客户端如何通过 MCP 与容器化服务进行通信
MCP datalog:预构建的安全 MCP 服务器
包含内容:
不断增长的 100 多个经 Docker 验证的 MCP 服务器库,包括:
- Stripe
- LangChain
- Elastic
- Pinecone
- Hugging Face
主要特性:
每个 MCP 服务器运行在容器内,包含:
- OpenAPI 规范
- 安全的默认配置
- Docker Desktop 集成
开发者为何关注:
- AI Agent 的即插即用工具
- 跨服务一致的开发体验
可视化概览:
Docker Desktop 集成 MCP 目录
MCP 工具包:构建您专属的安全 MCP 服务器
工具包命令行功能:
mcp init→ 快速搭建新 MCP 服务器mcp run→ 运行本地开发版本mcp deploy→ 部署至 Docker 桌面版
安全特性:
- 容器隔离
- 支持 OAuth 凭证认证
- 可选速率限制与追踪功能
演示操作流程:
npm install -g @docker/mcp-toolkit
mcp init my-weather-api
cd my-weather-api
mcp run
可视化操作指南
MCP 工具包工作流程:从命令行到容器
将 MCP 服务器连接至 AI 客户端
支持的客户端:
- Claude (Anthropic)
- GPT Agents (OpenAI)
- Docker AI (beta)
- VS Code Extensions
运作原理:
- 智能体调用 MCP 规范中定义的
/invoke端点。 - 安全令牌交换处理身份验证。
- 响应返回给模型进行推理/执行。
用例示例:
Claude 在电商交互过程中通过 Docker MCP 服务器调用 Stripe 支付处理容器
可视化流程:
Shows how Claude securely calls a Stripe service via Docker MCP. 展示 Claude 如何通过 Docker MCP 安全调用 Stripe 服务
MCP 服务器开发者的最佳实践
Security: 安全性:
- 切勿使用 root 容器
- 使用
docker scan和trivy进行镜像漏洞扫描 - 使用 Docker 的密钥管理器(或 Vault)存储敏感信息
Performance: 性能优化:
- 保持容器轻量化(使用 Alpine 或 Distroless 镜像)
- 使用流式响应进行 LLM 交互
Testing tips: 测试技巧:
- 使用
Postman+curl测试/invoke端点 - 使用
swagger-cli对 OpenAPI 规范进行代码检查
MCP 的未来发展方向
Predictions: 未来展望:
- Docker AI 仪表板集成
- MCP 编排(每个智能体支持多服务)
- AI 原生 DevOps(通过 MCP 服务器构建基础设施的智能体)
开发者机遇:
- 为开放的 MCP 服务器贡献力量
- 提交至 Docker 应用目录
- 构建供内部或公共使用的智能体工具
结语
Docker 的 MCP 目录与工具包仍处于测试阶段,但发展方向已然明确:AI 应用需要接入现实世界工具,而 Docker 正在构建一个安全开放的生态系统来支撑这一需求。
无论您正在开发智能体框架,还是仅仅尝试使用工具的 LLMs,现在都是参与其中的绝佳时机。
有什么想看到的 MCP 服务器创意?或者考虑贡献你自己的点子?我很乐意听取你的想法!😊
2 - A2A
2.1.1 - A2A 核心概念
https://google-a2a.github.io/A2A/topics/key-concepts/
其他内容待继续
Agent2Agent(A2A)协议是围绕一组定义代理如何交互的核心概念构建的。理解这些概念对于开发或集成 A2A 兼容系统至关重要。
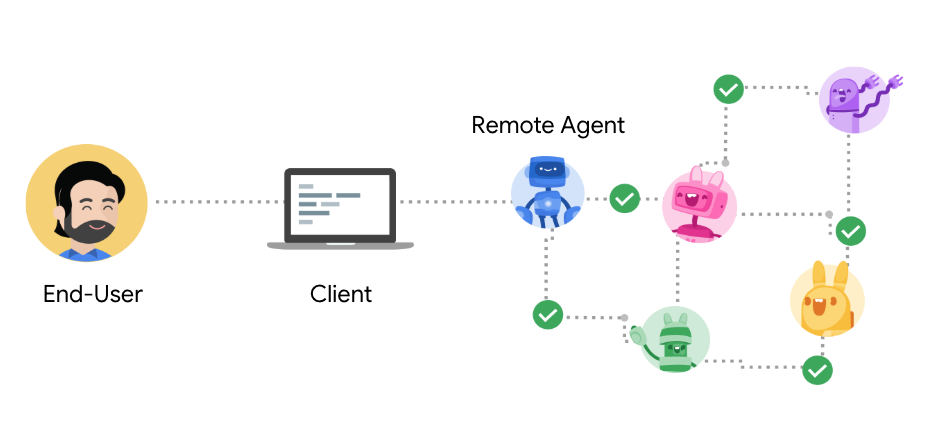
核心参与者
- User: 发起需要 agent 协助的请求或目标的最终用户(人工或自动服务)。
- A2A 客户端(客户端代理): 代表用户向远程代理请求操作或信息的应用程序、服务或其他 AI 代理。客户端使用 A2A 协议发起通信。
- A2A 服务器(远程代理): 一个 AI 代理或代理系统,公开实现 A2 A 协议的 HTTP 端点。它接收来自客户端的请求,处理任务,并返回结果或状态更新。从客户端的角度来看,远程代理作为一个“不透明”系统运行,这意味着客户端不需要知道它的内部工作、内存或工具。
基本通信元素
-
Agent Card: 代理卡
- JSON 元数据文档,通常可在众所周知的 URL(例如,/.well-known/agent.json),它描述了 A2 A 服务器。
- 它详细说明了代理的身份(名称、描述)、服务端点 URL、版本、支持的 A2A 功能(如流或推送通知)、它提供的特定技能、默认输入/输出模式和身份验证要求。
- 客户使用代理卡来发现代理并了解如何安全有效地与他们互动。
- 详见方案规范:代理卡 。
-
Task: 任务
- 当客户端向代理发送消息时,代理可以确定满足请求需要完成有状态任务(例如,“生成报告”、“预订航班”、“回答问题”)。
- 每个任务都有一个由代理定义的唯一 ID,并在定义的生命周期中进行(例如, 已提交 、 正在工作 、 需要输入 、 已完成 、 失败 )。
- 任务是有状态的,可以涉及客户端和服务器之间的多个交换(消息)。
- 详见协议规范:任务对象 。
-
消息
- 表示客户端和代理之间的单轮或单单元通信。
- 消息有一个角色 (客户端发送消息的 “用户” 或服务器发送消息的 “代理”),并包含一个或多个携带实际内容的 Part 对象。Message 对象的 messageId 部分是由消息的发送者为每个消息设置的唯一标识符。
- 用于传达不一定是正式工件的指令、上下文、问题、答案或状态更新。
- 详见协议规范:消息对象 。
-
部件
- 消息或文件中内容的基本单位。每个部分都有特定的类型 ,并且可以携带不同类型的数据:
- TextPart:包含纯文本内容。
- FilePart:表示一个文件,它可以作为内联 base64 编码的字节传输,也可以通过 URI 引用。包括文件名和媒体类型等元数据。
- DataPart:携带结构化 JSON 数据,用于表单、参数或任何机器可读信息。
- 详见协议规范:部件对象 。
-
Artifact
- 表示远程代理在任务处理期间生成的有形输出或结果。
- 示例包括生成的文档、图像、电子表格、结构化数据结果或作为任务的直接结果的任何其他自包含信息。
- 工件由一个或多个 Part 对象组成,并且可以以增量方式流式传输。
- 详见协议规范:工件对象 。
交互机制
Request/Response (Polling)
请求/响应(轮询):
-
客户端发送请求(例如,使用消息/发送 RPC 方法)并从服务器接收响应。
-
如果交互需要一个有状态的长时间运行的任务,服务器最初可能会响应一个工作状态。客户端然后将周期性地调用 tasks/get 以轮询更新,直到任务到达终端状态(例如, 完成 , 失败 )。
流(服务器发送事件- SSE)
2.1.2 - 什么是 A2A?
https://medium.com/@akash22675/what-is-a2a-agent-to-agent-protocol-d2325a41633a
代理到代理协议(Agent to Agent Protocol / A2A) 是一个标准化的通信框架,使 AI agent 代理能够以一致、可预测的方式相互交互。A2A 由 Google 发布,并被包括 Intuitive,LangChain 和 MongoDB 在内的多家公司采用,它为不同的 AI agent 提供了基础设施,以便在复杂的任务上进行有效的协作。

A2A 协议的核心概念
A2A 解决了什么问题?
在现代人工智能应用中,复杂的任务通常需要多个专业代理的专业知识。例如,计划旅行可能涉及专门从事机票预订,酒店推荐和当地活动的代理商。如果没有标准化的协议,这些代理中的每一个都需要自定义集成代码来相互通信,从而导致:
- 不一致的通信模式
- 不兼容的数据格式
- 维护和更新困难
- 有限的互操作性
A2A 通过为代理建立标准方法来解决这些问题:
- 发现彼此的能力
- 交换信息
- 协作处理任务
- 处理错误和异常
A2A 与 MCP(模型上下文协议)
虽然这些协议看起来相似,但它们用于不同的目的:

-
MCP(Model Context Protocol)
专注于语言模型如何与工具和资源(如 API、数据库和知识源)进行通信。把 MCP 看作是机械师如何与他们的工具进行交互,您可以在这里阅读更多上下文。
-
A2A
A2A(Agent to Agent Protocol):专注于完整的代理(每个代理包含一个 LLM 加上工具)如何相互通信。A2A 是机械师与客户或零件供应商沟通的方式。
一个有用的类比:如果一个代理就像一个汽车维修人员(LLM)与他们的工具箱(通过 MCP 连接的工具),那么 A2A 定义了这个汽车维修人员如何与客户,零件供应商和其他专家进行沟通。
A2A 的主要组成部分
Agent Card
代理卡是代理用来向其他代理通告其能力的标准化描述。将 Agent Card 视为名片或个人资料,其中包括:

代理卡示例(JSON 格式):
{
"name": "Google Maps Agent",
"description": "An agent that helps with map-related tasks",
"url": "https://maps-agent.example.com",
"provider": {
"name": "Google",
"url": "https://google.com"
},
"capabilities": [
{
"type": "route_planning",
"description": "Plan routes between locations"
},
{
"type": "custom_map",
"description": "Create custom maps with points of interest"
}
]
}
代理发现
为了让代理进行协作,它们首先需要发现彼此。A2A 支持多种发现方法:

- 基于 DNS 的发现 :客户端可以通过解析域名找到 agent.json 文件来发现代理。
- 基于注册表的发现 :应用程序维护受信任代理的注册表。
- 私有发现 :已知代理端点的直接配置。
任务处理流程
A2A 协议定义了代理之间的任务处理的标准流程:

A2A 中的任务遵循标准格式,通常用 JSON 表示:
{
"task": {
"input": "Tell me a joke",
"instructions": "Generate a short, family-friendly joke"
}
}
通信协议
A2A 基于已建立的通信协议:
- HTTP/HTTPS:用于基本的请求/响应通信
- JSON-RPC:用于结构化方法调用
- 服务器发送事件(Server-Sent Events / SSE):用于流响应
- JSON:作为标准数据交换格式
高级功能
A2A 支持多个高级功能,可实现强大的 agent 交互:
- 多模式通信 :处理文本、图像、音频和其他数据类型
- 流 :对长时间运行的任务进行实时流响应
- 错误处理 :标准化的错误格式,以便更好地调试
- 澄清请求 :agent 提出后续问题的能力

实用 A2A 实现
让我们看看 A2A 在实际实现中的样子:
示例:报销代理
// Agent Card Definition
const agentCard = {
name: "Expense Reimbursement Agent",
description: "An agent that processes expense reimbursement requests",
url: "https://reimbursement.example.com",
provider: {
name: "Financial Services Inc.",
url: "https://financial-services.example.com"
},
capabilities: [
{
type: "process_reimbursement",
description: "Process expense receipts and generate reimbursement forms"
}
]
};
// Agent Implementation
class ReimbursementAgent {
constructor() {
this.llm = new GeminiModel("gemini-2.0-flash");
this.tools = [
new ReceiptParser(),
new PolicyValidator(),
new FormGenerator()
];
}
async processTask(task) {
// Process the task using LLM and tools
const parsedReceipt = await this.tools[0].execute(task.input);
const validationResult = await this.tools[1].execute(parsedReceipt);
if (validationResult.needsClarification) {
return {
type: "clarification_request",
question: validationResult.question
};
}
const reimbursementForm = await this.tools[2].execute(validationResult);
return {
type: "task_complete",
result: reimbursementForm
};
}
}
真实世界的 A2A 工作流程示例
为了更好地理解 A2A 的实际应用,让我们来看看一个真实的示例:

在本例中:
- HR 经理在 Google Agent Workspace 中与客户端代理交互
- 客户端代理发现并与专门的代理进行通信,以确定候选人来源和安排面试
- 代理商在需要时提出澄清问题
- 每个代理使用自己的工具和资源执行其专门功能
- 客户端代理协调整个工作流并将结果呈现给用户
A2A 协议的优点
- 标准化通信 :代理交互的一致方式,无需自定义集成
- 可组合性 :易于联合专用代理以执行复杂任务
- 发现 :发现可用代理及其能力的机制
- 互操作性 :来自不同提供商的代理可以一起工作
- 可扩展性 :新的代理类型可以加入生态系统
现状和未来潜力
Agent to Agent Protocol 仍处于早期阶段,最近由 Google 发布。虽然许多公司已经开始采用该协议,但该协议的全面影响和演变将随着时间的推移而展开。
主要发展领域包括:
- 安全和认证标准
- 更复杂的代理发现机制
- 高级错误处理和恢复
- 跨平台代理兼容性
- 与现有 AI 生态系统的整合
Agent to Agent Protocol(A2A)是创建更具协作性的人工智能生态系统的重要一步。通过标准化代理之间的通信方式,A2A 可以实现更复杂的多代理解决方案,而无需为每个代理配对进行自定义集成。
2.2 - A2A Card
3 - Agent Skills
3.1 - Agent Skills文章
3.1.1 - 为智能体配备 Agent Skills 以适应真实世界
基本信息:
-
英文原文: https://www.anthropic.com/engineering/equipping-agents-for-the-real-world-with-agent-skills
-
中文翻译:
Claude is powerful, but real work requires procedural knowledge and organizational context. Introducing Agent Skills, a new way to build specialized agents using files and folders.
Claude 很强大,但实际工作需要程序性知识和组织背景。介绍 Agent Skills,这是一种使用文件和文件夹构建专业化 agents 的新方法。
As model capabilities improve, we can now build general-purpose agents that interact with full-fledged computing environments. Claude Code, for example, can accomplish complex tasks across domains using local code execution and filesystems. But as these agents become more powerful, we need more composable, scalable, and portable ways to equip them with domain-specific expertise.
随着模型能力的提升,我们现在可以构建与完整计算环境交互的通用 agents。例如,Claude Code 可以使用本地代码执行和文件系统在各个领域完成复杂任务。但随着这些 agents 变得更强大,我们需要更具组合性、可扩展性和便携性的方法来为它们配备特定领域的专业知识。
This led us to create Agent Skills: organized folders of instructions, scripts, and resources that agents can discover and load dynamically to perform better at specific tasks. Skills extend Claude’s capabilities by packaging your expertise into composable resources for Claude, transforming general-purpose agents into specialized agents that fit your needs.
这促使我们创建了 Agent Skills:有组织的指令、脚本和资源文件夹,agents 可以动态发现和加载这些内容以在特定任务中表现得更好。Skills 通过将您的专业知识打包成可组合的资源来扩展 Claude 的能力,将通用 agents 转变为符合您需求的专业化 agents。
Building a skill for an agent is like putting together an onboarding guide for a new hire. Instead of building fragmented, custom-designed agents for each use case, anyone can now specialize their agents with composable capabilities by capturing and sharing their procedural knowledge. In this article, we explain what Skills are, show how they work, and share best practices for building your own.
为 agent 构建 skill 就像为新员工准备入职指南。现在,任何人都可以通过捕获和共享他们的程序性知识,使用可组合的能力来专门化他们的 agents,而不必为每个用例构建零散的、定制设计的 agents。在本文中,我们将解释 Skills 是什么,展示它们如何工作,并分享构建自己的 Skills 的最佳实践。

A skill is a directory containing a SKILL.md file that contains organized folders of instructions, scripts, and resources that give agents additional capabilities.
一个 skill(技能) 是一个包含 SKILL.md 文件 的目录,其中组织了指令、脚本和资源等子文件夹,用来为 agent(智能体) 提供额外的能力。
Skill 的结构
To see Skills in action, let’s walk through a real example: one of the skills that powers Claude’s recently launched document editing abilities. Claude already knows a lot about understanding PDFs, but is limited in its ability to manipulate them directly (e.g. to fill out a form). This PDF skill lets us give Claude these new abilities.
为了看到 Skills 的实际效果,让我们通过一个真实的例子来说明:驱动 Claude 最近推出的文档编辑能力的技能之一。Claude 对理解 PDF 已经了解很多,但在直接操作它们方面受到限制(例如填写表单)。这个 PDF skill 让我们能够赋予 Claude 这些新能力。
At its simplest, a skill is a directory that contains a SKILL.md file. This file must start with YAML frontmatter that contains some required metadata: name and description. At startup, the agent pre-loads the name and description of every installed skill into its system prompt.
最简单来说,skill 是一个包含 SKILL.md 文件的目录。该文件必须以包含一些必需元数据的 YAML frontmatter 开始:name 和 description。在启动时,agent 会将每个已安装 skill 的 name 和 description 预加载到其系统提示中。
This metadata is the first level of progressive disclosure: it provides just enough information for Claude to know when each skill should be used without loading all of it into context. The actual body of this file is the second level of detail. If Claude thinks the skill is relevant to the current task, it will load the skill by reading its full SKILL.md into context.
这个元数据是 渐进式披露 的第一级:它提供足够的信息让 Claude 知道何时应该使用每个 skill,而无需将所有内容加载到上下文中。该文件的实际主体是细节的第二级。如果 Claude 认为 skill 与当前任务相关,它将通过读取完整的 SKILL.md 到上下文中来加载该 skill。

A SKILL.md file must begin with YAML Frontmatter that contains a file name and description, which is loaded into its system prompt at startup.
一个 SKILL.md 文件必须以 YAML Frontmatter(前置说明块) 开头,其中包含文件名和描述信息,这些内容会在启动时加载到智能体的 system prompt(系统提示词) 中。
As skills grow in complexity, they may contain too much context to fit into a single SKILL.md, or context that’s relevant only in specific scenarios. In these cases, skills can bundle additional files within the skill directory and reference them by name from SKILL.md. These additional linked files are the third level (and beyond) of detail, which Claude can choose to navigate and discover only as needed.
随着 skills 变得越来越复杂,它们可能包含太多上下文无法放入单个 SKILL.md 中,或者包含仅在特定场景中相关的上下文。在这些情况下,skills 可以在 skill 目录中捆绑其他文件,并从 SKILL.md 中按名称引用它们。这些额外的链接文件是细节的第三级(及更高级别),Claude 可以选择仅在需要时导航和发现。
In the PDF skill shown below, the SKILL.md refers to two additional files (reference.md and forms.md) that the skill author chooses to bundle alongside the core SKILL.md. By moving the form-filling instructions to a separate file (forms.md), the skill author is able to keep the core of the skill lean, trusting that Claude will read forms.md only when filling out a form.
在下面显示的 PDF skill 中,SKILL.md 引用了两个额外文件(reference.md 和 forms.md),skill 作者选择将它们与核心 SKILL.md 捆绑在一起。通过将表单填写指令移到单独的文件(forms.md)中,skill 作者能够保持 skill 的核心精简,相信 Claude 只在填写表单时才会读取 forms.md。

You can incorporate more context (via additional files) into your skill that can then be triggered by Claude based on the system prompt.
你可以在技能中加入更多上下文信息(通过额外的文件实现),这些文件可以根据系统提示词由 Claude 自动触发使用。
Progressive disclosure is the core design principle that makes Agent Skills flexible and scalable. Like a well-organized manual that starts with a table of contents, then specific chapters, and finally a detailed appendix, skills let Claude load information only as needed:
渐进式披露是使 Agent Skills 灵活和可扩展的核心设计原则。就像一本组织良好的手册,从目录开始,然后是特定章节,最后是详细的附录,skills 让 Claude 仅在需要时加载信息:

Agents with a filesystem and code execution tools don’t need to read the entirety of a skill into their context window when working on a particular task. This means that the amount of context that can be bundled into a skill is effectively unbounded.
拥有文件系统和代码执行工具的 agents 在处理特定任务时不需要将整个 skill 读入上下文窗口。这意味着可以捆绑到 skill 中的上下文量实际上是无限的。
Skills 和上下文窗口
The following diagram shows how the context window changes when a skill is triggered by a user’s message.
下面的图表显示了当用户的消息触发 skill 时上下文窗口如何变化。

Skills are triggered in the context window via your system prompt.
Skills 通过您的系统提示在上下文窗口中触发。
The sequence of operations shown:
- To start, the context window has the core system prompt and the metadata for each of the installed skills, along with the user’s initial message;
- Claude triggers the PDF skill by invoking a Bash tool to read the contents of
pdf/SKILL.md; - Claude chooses to read the
forms.mdfile bundled with the skill; - Finally, Claude proceeds with the user’s task now that it has loaded relevant instructions from the PDF skill.
显示的操作序列如下:
- 开始时,上下文窗口包含核心系统提示和每个已安装 skill 的元数据,以及用户的初始消息;
- Claude 通过调用 Bash 工具读取 pdf/SKILL.md 的内容来触发 PDF skill;
- Claude 选择读取与该 skill 捆绑的 forms.md 文件;
- 最后,Claude 继续处理用户的任务,因为它已经从 PDF skill 加载了相关指令。
Skills 和代码执行
Skills can also include code for Claude to execute as tools at its discretion.
Skills 还可以包含代码供 Claude 在其判断下作为工具执行
Large language models excel at many tasks, but certain operations are better suited for traditional code execution. For example, sorting a list via token generation is far more expensive than simply running a sorting algorithm. Beyond efficiency concerns, many applications require the deterministic reliability that only code can provide.
大语言模型在许多任务上表现出色,但某些操作更适合传统的代码执行。例如,通过 token 生成对列表进行排序比简单地运行排序算法要昂贵得多。除了效率问题外,许多应用程序需要只有代码才能提供的确定性可靠性。
In our example, the PDF skill includes a pre-written Python script that reads a PDF and extracts all form fields. Claude can run this script without loading either the script or the PDF into context. And because code is deterministic, this workflow is consistent and repeatable.
在我们的例子中,PDF skill 包含一个预先编写的 Python 脚本,可以读取 PDF 并提取所有表单字段。Claude 可以运行此脚本,而无需将脚本或 PDF 加载到上下文中。而且因为代码是确定性的,这个工作流程是一致且可重复的。

Skills can also include code for Claude to execute as tools at its discretion based on the nature of the task.
Skills 还可以包含代码,供 Claude 根据任务的性质自行决定作为工具来执行。
开发和评估 Skills
Here are some helpful guidelines for getting started with authoring and testing skills:
- Start with evaluation: Identify specific gaps in your agents’ capabilities by running them on representative tasks and observing where they struggle or require additional context. Then build skills incrementally to address these shortcomings.
- Structure for scale: When the
SKILL.mdfile becomes unwieldy, split its content into separate files and reference them. If certain contexts are mutually exclusive or rarely used together, keeping the paths separate will reduce the token usage. Finally, code can serve as both executable tools and as documentation. It should be clear whether Claude should run scripts directly or read them into context as reference. - Think from Claude’s perspective: Monitor how Claude uses your skill in real scenarios and iterate based on observations: watch for unexpected trajectories or overreliance on certain contexts. Pay special attention to the
nameanddescriptionof your skill. Claude will use these when deciding whether to trigger the skill in response to its current task. - Iterate with Claude: As you work on a task with Claude, ask Claude to capture its successful approaches and common mistakes into reusable context and code within a skill. If it goes off track when using a skill to complete a task, ask it to self-reflect on what went wrong. This process will help you discover what context Claude actually needs, instead of trying to anticipate it upfront.
以下是一些有助于开始编写和测试 skills 的指导原则:
-
从评估开始: 通过在代表性任务上运行您的 agents 并观察它们在哪些方面遇到困难或需要额外上下文来识别其能力中的具体差距。然后逐步构建 skills 来解决这些不足。
-
为可扩展性构建结构: 当 SKILL.md 文件变得过于庞大时,将其内容拆分为单独文件并引用它们。如果某些上下文相互排斥或很少一起使用,保持路径分离将减少 token 使用量。最后,代码既可以作为可执行工具,也可以作为文档。应该明确 Claude 应该直接运行脚本还是将它们读入上下文作为参考。
-
从 Claude 的角度思考: 监控 Claude 在实际场景中如何使用您的 skill,并根据观察进行迭代:注意意外的轨迹或对某些上下文的过度依赖。特别关注您 skill 的 name 和 description。Claude 在决定是否响应其当前任务触发 skill 时会使用这些信息。
-
与 Claude 一起迭代: 当您与 Claude 合作完成任务时,请要求 Claude 将其成功方法和常见错误捕获到 skill 中的可重用上下文和代码中。如果在使用 skill 完成任务时偏离轨道,请它自我反思出了什么问题。这个过程将帮助您发现 Claude 实际需要什么上下文,而不是试图预先预测它。
使用 Skills 时的安全考虑
Skills provide Claude with new capabilities through instructions and code. While this makes them powerful, it also means that malicious skills may introduce vulnerabilities in the environment where they’re used or direct Claude to exfiltrate data and take unintended actions.
Skills 通过指令和代码为 Claude 提供新能力。虽然这使它们变得强大,但也意味着恶意 skills 可能在其使用的环境中引入漏洞,或指示 Claude 渗透数据并采取意外操作。
We recommend installing skills only from trusted sources. When installing a skill from a less-trusted source, thoroughly audit it before use. Start by reading the contents of the files bundled in the skill to understand what it does, paying particular attention to code dependencies and bundled resources like images or scripts. Similarly, pay attention to instructions or code within the skill that instruct Claude to connect to potentially untrusted external network sources.
我们建议只从可信来源安装 skills。当从不太可信的来源安装 skill 时,请在使用前彻底审核它。首先阅读 skill 中捆绑的文件内容以了解其功能,特别关注代码依赖项和捆绑资源(如图像或脚本)。同样,要注意 skill 中指示 Claude 连接到潜在不可信外部网络源的指令或代码。
Skills 的未来
Agent Skills are supported today across Claude.ai, Claude Code, the Claude Agent SDK, and the Claude Developer Platform.
Agent Skills 目前在 Claude.ai、Claude Code、Claude Agent SDK 和 Claude Developer Platform 上都受到支持。
In the coming weeks, we’ll continue to add features that support the full lifecycle of creating, editing, discovering, sharing, and using Skills. We’re especially excited about the opportunity for Skills to help organizations and individuals share their context and workflows with Claude. We’ll also explore how Skills can complement Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers by teaching agents more complex workflows that involve external tools and software.
在接下来的几周内,我们将继续添加支持创建、编辑、发现、共享和使用 Skills 完整生命周期的功能。我们对 Skills 帮助组织和个人与 Claude 共享其上下文和工作流程的机会特别感到兴奋。我们还将探索 Skills 如何通过教授 agents 涉及外部工具和软件的更复杂工作流程来补充 Model Context Protocol (MCP) 服务器。
Looking further ahead, we hope to enable agents to create, edit, and evaluate Skills on their own, letting them codify their own patterns of behavior into reusable capabilities.
展望未来,我们希望让 agents 能够自己创建、编辑和评估 Skills,让它们将自己的行为模式编码为可重用的能力。
Skills are a simple concept with a correspondingly simple format. This simplicity makes it easier for organizations, developers, and end users to build customized agents and give them new capabilities.
Skills 是一个简单的概念,具有相应简单的格式。这种简单性使组织、开发人员和最终用户更容易构建定制化的 agents 并为它们提供新能力。
We’re excited to see what people build with Skills. Get started today by checking out our Skills docs and cookbook.
我们很高兴看到人们用 Skills 构建什么。今天就开始,查看我们的 Skills 文档和 cookbook。



